Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed. Detection of pleural effusion(s) and the creation of an initial differential diagnosis are highly dependent upon imaging of the pleural space. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. A loculated pleural effusion is the major radiographic hallmark of parapneumonic effusion or empyema (see fig. Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity. Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart. It can also be life threatening. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural. If none is present the fluid is virtually always a transudate.
The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the. Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. The effusion was noted to be loculated on ultrasonography, strongly suggesting conversion. Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity.

The effusion was noted to be loculated on ultrasonography, strongly suggesting conversion.
Pleural fluid/serum protein ratio >0.5. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. Zaid zoumot, mbbs, ali s. Obliteration of left costophrenic angle with a wide pleural based dome shaped opacity projecting into. Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed. Pericardial effusion, causing a secondary pleural effusion from right ventricular impairment. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. Pleural effusions can loculate as a result of adhesions. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural.
Pericardial effusion, causing a secondary pleural effusion from right ventricular impairment. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity between the lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity (i.e., the visceral and parietal pleurae). Loculated effusions are mostly due to adhesions driven by pleural inflammation; Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural. More than one half of these massive. Zaid zoumot, mbbs, ali s. In transudative effusion, specific gravity is below 1.015 and.

Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures.
Wahla, mbbs and samar farha, md. Pleural infection pleural inflammation pleural malignancy (most often pleural fluid analysis findings: Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural. Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung. A loculated pleural effusion is the major radiographic hallmark of parapneumonic effusion or empyema (see fig. A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. Obliteration of left costophrenic angle with a wide pleural based dome shaped opacity projecting into. Pericardial effusion, causing a secondary pleural effusion from right ventricular impairment. Learn about different types of pleural effusions, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. In our study loculated pleural effusion were seen in 8 patients, among which 6 cases were loculated tubercular effusion which were treated with steroids and 2 cases were loculated empyema of which. Pleural fluid/serum protein ratio >0.5. Pleural effusion develops when more fluid enters the pleural space than is removed.
Pleural effusions can loculate as a result of adhesions. Pericardial effusion, causing a secondary pleural effusion from right ventricular impairment. Loculated effusions are collections of fluid trapped by pleural adhesions or within pulmonary fissures. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. More than one half of these massive.
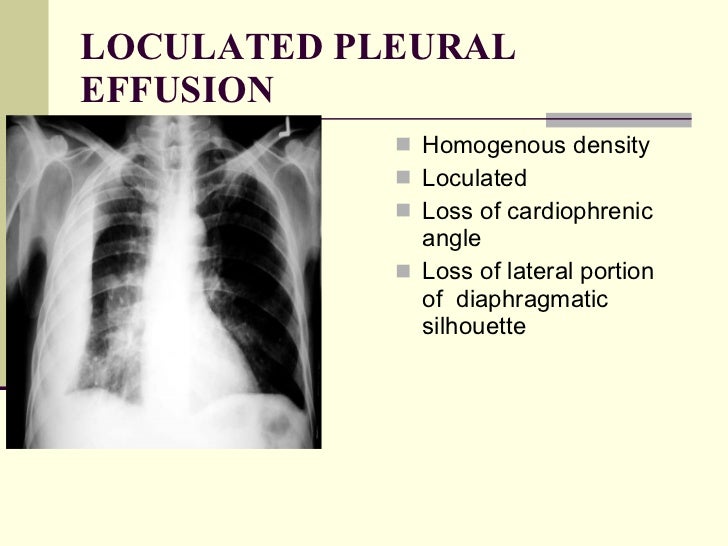
Causes of an exudative effusion are malignancy, infection, or inflammatory disorders such.
Pleural fluid/serum protein ratio >0.5. Learn about different types of pleural effusions, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. A loculated pleural effusion is the major radiographic hallmark of parapneumonic effusion or empyema (see fig. Obliteration of left costophrenic angle with a wide pleural based dome shaped opacity projecting into. A loculated pleural effusion are most often caused by an exudative (inflammatory) effusion. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudate and exudate based on the light criteria. Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart. Learn about pleural effusion (fluid in the lung) symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain. Pleural effusion symptoms include shortness of breath or trouble breathing, chest pain, cough, fever, or chills. Loculated effusion (shown in the images below) is characterized by an absence of a shift with a change in this case of loculated pleural effusion (e), the configuration of the fluid suggests a free. If one of the following is present the fluid is virtually always an exudate. Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal. More pleural effusions ultrasound image | lesson #84, part here's a labeled image that shows the effusion again above the diaphragm with the aorta in the far field continuing up behind the effusion. A role in selected clinical circumstances. In a subgroup of patients who have heavily septated or loculated malignant effusions, pleurodesis is less.

Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart.

Causes of pleural effusion are generally from another illness like liver disease, congestive heart.

Wahla, mbbs and samar farha, md.

Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal.

Wahla, mbbs and samar farha, md.

Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis.

It can also be life threatening.
.png)
Pleural effusions may result from pleural, parenchymal, or extrapulmonary disease.

Case contributed by dr prashant mudgal.

Pleural fluid/serum ldh ratio >0.6.

Pleural effusion refers to a buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest cavity.

A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.

Zaid zoumot, mbbs, ali s.

Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung.

Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural.

Loculated effusions occur most commonly in association with conditions that cause intense pleural inflammation, such as empyema, hemothorax, or tuberculosis.

The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural.

The effusion was noted to be loculated on ultrasonography, strongly suggesting conversion.

Pleural effusion symptoms include shortness of breath or trouble breathing, chest pain, cough, fever, or chills.

Learn about pleural effusion including causes of pleural effusion.

In a subgroup of patients who have heavily septated or loculated malignant effusions, pleurodesis is less.

Wahla, mbbs and samar farha, md.

Pleural infection pleural inflammation pleural malignancy (most often pleural fluid analysis findings:

The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the.

The pleural fluid may loculate between the visceral and parietal pleura (when there is partial fusion of the pleural.

Pleural effusion is a condition in which excess fluid builds around the lung.

Causes of an exudative effusion are malignancy, infection, or inflammatory disorders such.

0 Komentar